|
Insurance Coverage: What It Is, How It Works, and Why It Matters |
||
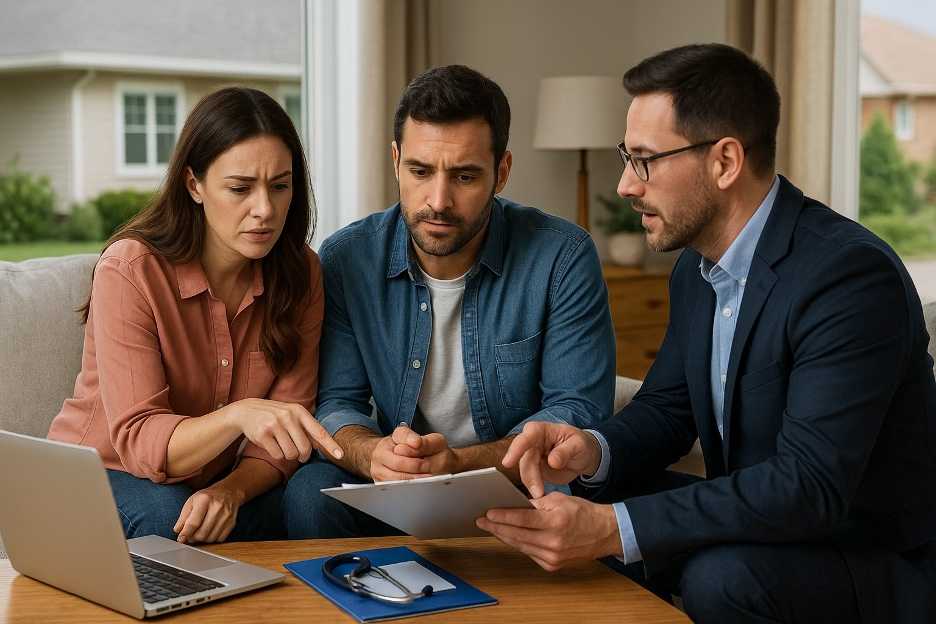 |
Insurance is a financial tool that protects individuals and businesses from unexpected losses by transferring risk to an insurer. Whether it’s health, auto, home, or life insurance, having the right policy ensures peace of mind and financial stability. Understanding the types, costs, and coverage options is key to making informed decisions.
What Is Insurance?Insurance is a contractual arrangement in which a person or entity pays a premium to an insurer in exchange for financial protection against specified risks. These risks might include property damage, personal injury, illness, or even death. The insurer agrees to compensate the insured, or a beneficiary, if a covered loss occurs. This concept of risk-sharing is essential for individuals and businesses alike. How Insurance WorksAt the heart of insurance is risk management. When you buy a policy, you’re transferring the financial burden of certain types of losses to a third party-the insurer. This transfer is legally binding and governed by the insurance contract (also called the policy).
For example, if your home is damaged by fire, your homeowners insurance policy will help cover the repair costs, subject to your deductible. Insurers determine premiums based on factors such as risk levels, claim history, age, location, and more. Types of Insurance and What They CoverHealth Insurance
Homeowners and Renters Insurance
Why Insurance Is EssentialInsurance acts as a financial safety net. For individuals, it prevents one unexpected event-such as a car accident or serious illness-from causing financial ruin. For businesses, it allows continuity and protects against liability and lawsuits. Understanding Premiums, Deductibles, and Coverage LimitsA premium is the amount you pay-monthly, quarterly, or annually-for coverage. Lower premiums often mean higher deductibles, which is the amount you must pay before the insurer covers the rest. Choosing the right balance depends on your financial situation and risk tolerance. How to Choose the Right InsuranceWhen shopping for insurance, consider the following:
Use licensed agents or online marketplaces to compare quotes and coverage levels. Also, check the insurer’s financial strength ratings from agencies like A.M. Best or Moody’s. Filing a ClaimFiling a claim involves notifying your insurer when a covered event occurs, documenting the loss, and completing the required forms. Most insurers offer digital claim submission. The timeline and process may vary, but prompt reporting and detailed records improve your chances of a smooth payout. Common Insurance Myths Debunked
How Insurance Impacts Your Financial PlanningInsurance is a core component of personal financial planning. It helps preserve wealth and avoid unexpected losses. A sound insurance strategy balances cost with protection and aligns with your life stage, assets, and dependents. The Future of Insurance: Trends to WatchInsurtech is revolutionizing the insurance industry with AI-powered underwriting, instant claims processing, and usage-based pricing. Consumers now have more control, flexibility, and transparency than ever. Insurance Final ThoughtsInsurance is more than a legal or financial obligation-it’s a powerful tool for protecting your life, property, health, and future. Whether you're purchasing your first policy or reviewing your current coverage, being informed empowers you to make confident, cost-effective choices.
|